As China navigates its ambitious transition to renewable energy, experts are indicating that the country needs to diversify its clean technology investments. Following previous successes in wind and solar energy, there is a growing consensus that reliance on these sectors alone will not be sufficient to meet future energy demands or carbon neutrality goals.
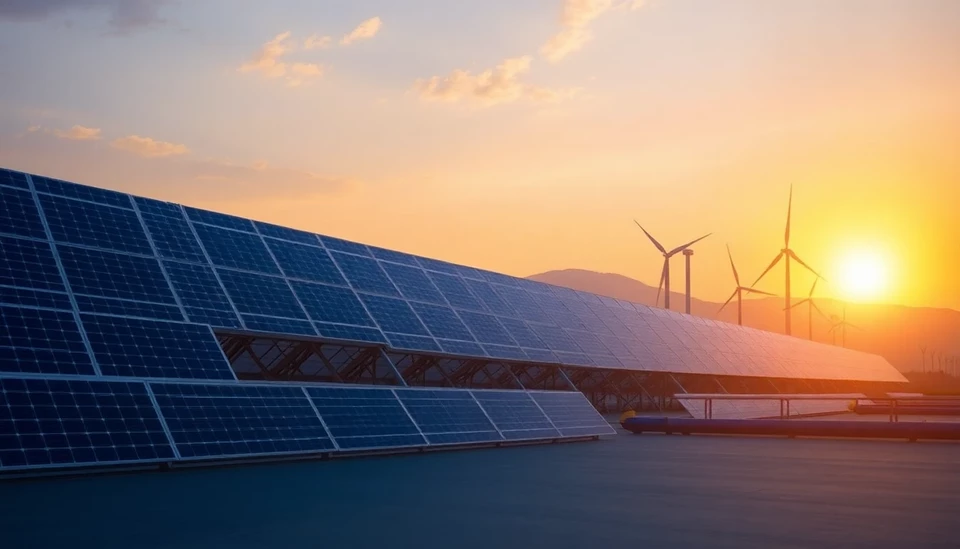
China's investments in clean technology over the past decade have led to remarkable advancements, positioning the country as a global leader in both solar panels and wind turbines. However, according to industry analysts and policymakers, the rapid growth in these areas has reached a pivotal moment. The installed capacity for solar and wind energy is now substantial, leading to what some are referring to as a saturation point. That’s prompting calls for increased focus on additional clean technologies, such as energy storage, hydrogen production, and electric vehicle infrastructure.
Critics argue that without a broader approach that includes various forms of clean energy, China may struggle to ensure energy security or achieve its ambitious carbon emission goals set for 2060. They warn that failure to invest in renewable energy diversification could limit the overall effectiveness of China’s green energy initiatives. This multifaceted approach to clean energy isn't just beneficial; it is essential for addressing potential challenges, such as grid stability and supply chain resilience during periods of high energy demand or low renewable output.
One area drawing particular attention is energy storage technology, which plays a crucial role in balancing energy supply and demand—particularly given the intermittent nature of solar and wind energy. Storage solutions, such as battery technology, are vital for maximizing the utility and efficiency of renewable resources. Investments in this sector not only promise to enhance the reliability of power supply but also pave the way for innovations in energy delivery systems.
Another focal point is the development of hydrogen as a clean fuel. As the country aims to decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors, including heavy industry and transportation, hydrogen could play a transformative role. With abundant renewable energy resources, China is well-positioned to become a leading producer of green hydrogen, which can be utilized in various industrial processes as well as in fuel cells for vehicles.
Furthermore, enhancing the infrastructure for electric vehicles is key to advancing the country's commitment to reduce emissions from the transportation sector. This would involve significant investments in charging networks and incentives for consumers to adopt electric vehicles, making the shift away from fossil fuels more attainable.
In summary, while China has made substantial strides in the fields of wind and solar energy, the journey toward a comprehensive clean energy future requires realignment and expansion of investment into emerging clean technologies. The emphasis should be not only on sustaining the current momentum but avoiding potential pitfalls that could derail progress.
As stakeholders from both the public and private sectors weigh in on these challenges, supportive policies and funding mechanisms will be crucial. Navigating this next phase of development will require a collective effort to innovate, invest, and ultimately transform China's energy landscape to create a more sustainable and resilient future.
#CleanEnergy #China #Renewables #EnergyStorage #Hydrogen #ElectricVehicles #SustainableDevelopment #GreenTech
Author: Megan Clarke