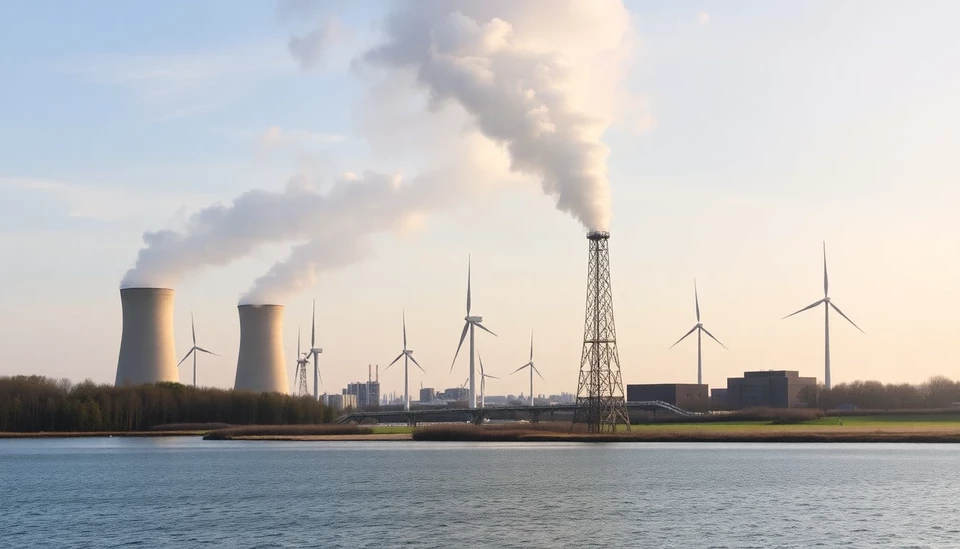
In a surprising turn of events, Germany's coal power generation has surged to its highest levels in one year, signaling a dramatic shift in the country's energy landscape. This uptick comes amidst a notable decline in wind energy production, which is traditionally one of the cornerstones of Germany's renewable energy strategy.
As reported recently, coal plants in Germany have ramped up their outputs significantly, contributing to approximately 30% of the country's energy mix. This resurgence in coal generation can be primarily attributed to the declining efficiency of wind farms during the winter months, exacerbated by less favorable weather conditions that have led to diminished wind speeds. Consequently, energy authorities have had to rely more heavily on coal, leading to concerns about climate goals and emissions targets.
According to data from industry sources, coal generation levels have reached their annual peak just as government policies aimed at phasing out coal by 2038 face increasing scrutiny. Lawmakers are urged to strike a balance between ensuring energy security during times of reduced renewable output and adhering to environmental commitments. Some analysts are concerned that this reliance on coal could stall or even reverse progress in the transition to a low-carbon energy system.
The recent fall in wind energy has raised critical questions about Germany's energy infrastructure and its capacity to adapt to variations in renewable energy supply. As the country works to meet its ambitious energy transition goals, a more robust energy storage and management system is essential to ensure that energy needs are met without regressing to more polluting energy sources.
Moreover, stakeholders in the energy sector are calling for a renewed focus on diversifying energy sources and enhancing grid flexibility. With the volatility of weather-driven energy generation, coal has become a fallback option, but the long-term implications for climate change could be severe if dependency on fossil fuels is not curtailed promptly.
The rise in coal energy usage underscores the challenges faced by many countries striving to implement a green energy transition while fulfilling immediate energy demands. As nations like Germany lead the charge toward a renewable future, they must navigate the complexities of energy transformation, environmental responsibility, and economic viability.
This situation highlights the critical importance of developing resilient energy systems that can withstand fluctuations in renewable energy sourcing. Policymakers now face the urgent task of addressing these challenges while ensuring that the commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions remains at the forefront of their energy strategies.
As the energy debate continues in Germany, it is evident that balancing short-term needs with long-term sustainability goals will be pivotal in shaping the future of the country’s energy landscape.
#Germany #CoalPower #RenewableEnergy #WindEnergy #EnergyTransition #ClimateChange #EnergyPolicy #Sustainability
Author: Megan Clarke