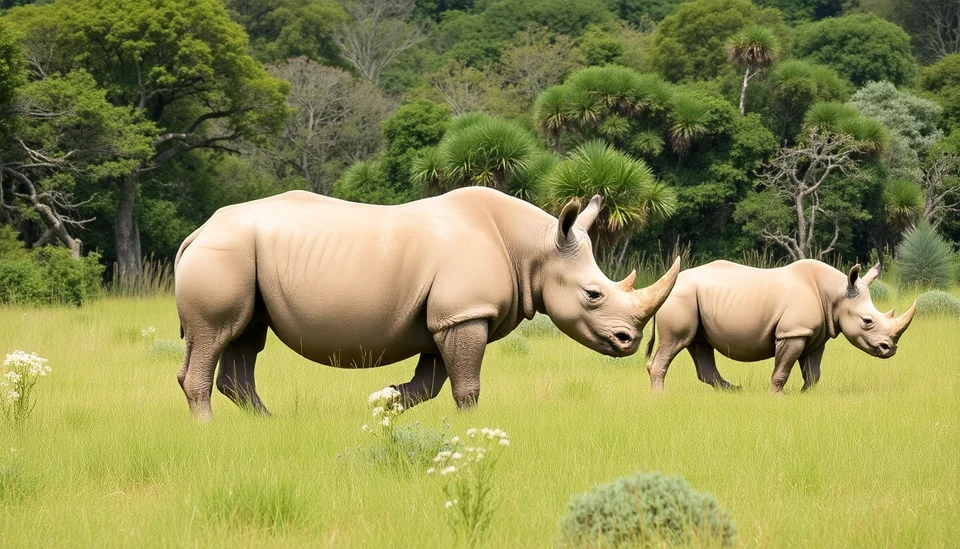
Kenya is embarking on an unprecedented reproductive program aimed at saving the critically endangered northern white rhinos, a subspecies facing imminent extinction. The government, alongside conservationists and wildlife organizations, is deploying advanced in vitro fertilization (IVF) techniques to ensure the survival of these magnificent creatures.
Currently, only two northern white rhinos exist in the world, both females, residing at the Ol Pejeta Conservancy in Laikipia County, Kenya. With their natural breeding capabilities severely limited, this innovative approach is being hailed as the last hope for reviving the population of a subspecies that once roamed freely across parts of East and Central Africa.
The conservation initiative is not entirely new, as it draws upon previous efforts to use IVF techniques for various species facing the brink of extinction. However, this particular project marks a significant leap in the use of technology to protect biodiversity and combat the rising threats posed by poaching and habitat loss.
Kenya's government has green-lighted the allocation of approximately 5 million Kenyan shillings ($43,000) toward this endeavor. The funds will support research, veterinary care, and the establishment of a laboratory dedicated to the development of effective reproductive techniques tailored specifically for the northern white rhino.
One of the key players in this ambitious project is the Southern White Rhino population, which serves as a genetic reservoir for the northern white rhinos. By collecting and storing viable sperm from Southern White Rhinos, conservationists aim to facilitate the creation of embryos that can be implanted into surrogate Southern White Rhino mothers, which will hopefully give birth to calves carrying the northern white rhino lineage.
The initiative has garnered global attention, with wildlife experts and enthusiasts expressing cautious optimism about the potential outcomes. There remain vast challenges ahead, including the complex nature of IVF procedures and ensuring the health and stability of both the surrogate and the embryos.
In addition to the IVF aspect, the conservation strategy focuses on broader protective measures. This includes intensive anti-poaching efforts, habitat restoration, and community engagement initiatives aimed at fostering coexistence between local populations and wildlife. Educational programs will raise awareness about the plight of the northern white rhinos, emphasizing the importance of their preservation not just for ecological reasons, but also for cultural heritage.
As the world continues to battle the impacts of climate change and habitat destruction, Kenya's innovative approach to wildlife conservation could establish a new frontier in species preservation. The outcome of this groundbreaking project may serve as a beacon of hope, inspiring similar efforts worldwide to protect other endangered species from the brink of extinction.
In conclusion, while hurdles lie ahead, the collective determination of Kenyan authorities, conservationists, and the international community could lead to a remarkable turnaround in the fate of the northern white rhino, reaffirming the planet’s commitment to preserving its precious biodiversity.
#Kenya #WildlifeConservation #NorthernWhiteRhino #IVF #EndangeredSpecies #Biodiversity #NatureProtection #ConservationEfforts
Author: Megan Clarke