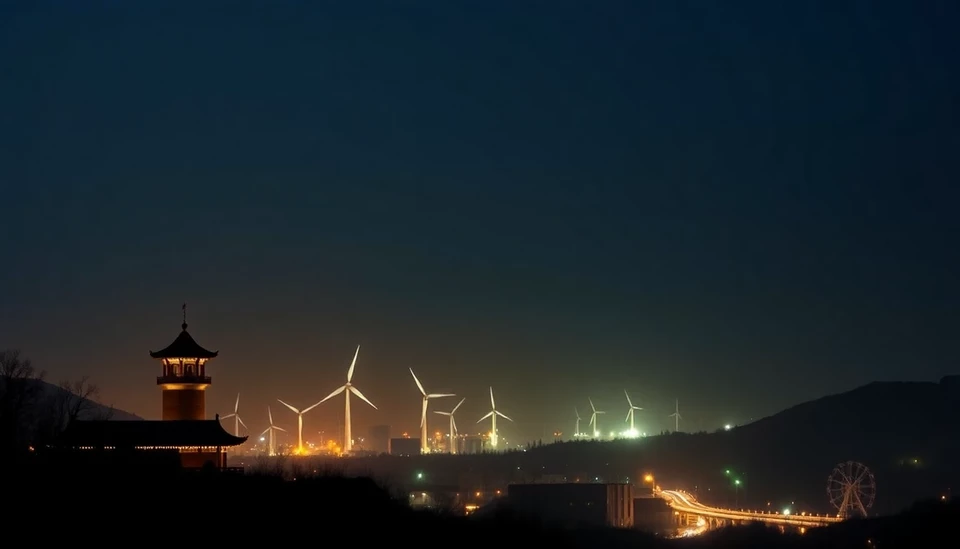
In a bold initiative aimed at bolstering its sustainability efforts, the Chinese government has announced a plan to reduce energy consumption per unit of GDP by 3% in the year 2025. This decision comes as part of China’s ongoing commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2060 while simultaneously addressing the pressing issue of environmental sustainability.
The announcement highlights a significant shift in China’s energy use strategy, emphasizing the importance of optimizing energy efficiency across various sectors of the economy. By decreasing energy intensity—defined as the amount of energy consumed per unit of GDP—China aims to foster economic growth while minimizing its environmental impact. This move is seen as critical as the nation continues to grapple with the dual challenges of economic expansion and climate change mitigation.
Analysts suggest that this policy reflects a broader trend in global energy consumption, where countries are increasingly seeking to decouple economic growth from energy use. China, as the world’s largest emitter of carbon dioxide, plays a vital role on the international stage, and its new target could potentially set a precedent for other nations to follow.
In 2022, China recorded a 2.7% reduction in energy intensity as part of its previous commitments, showcasing its ability to alter consumption patterns strategically. This success lays the groundwork for the new goal, as authorities aim to leverage technological advancements and transition towards more energy-efficient practices in industrial operations, transportation, and infrastructure development.
As part of the agenda, the government intends to implement stricter policies governing energy use, focusing on promoting renewable energies alongside investments in cleaner technologies. The move is likely to catalyze innovation and encourage enterprises to adopt practices that not only meet regulatory demands but also appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers.
This energy reform is expected to have broader implications not just domestically but internationally as well. With the global community increasingly attentive to sustainability, China's commitment may enhance its standing as a leader in environmental policy. Moreover, such measures could impact global energy markets, particularly as China continues to be a dominant force in various sectors, including manufacturing and green technology.
In conclusion, China’s pledge to reduce energy use per unit of GDP by 3% by 2025 represents a significant stride towards balancing economic growth and environmental stewardship. As the country navigates this complicated landscape, the implications of its policies will be closely watched by environmentalists, economists, and policymakers around the world.
#China #EnergyEfficiency #Sustainability #CarbonNeutrality #CleanEnergy #EconomicGrowth #ClimateChange #EnergyUsePerGDP
Author: John Harris