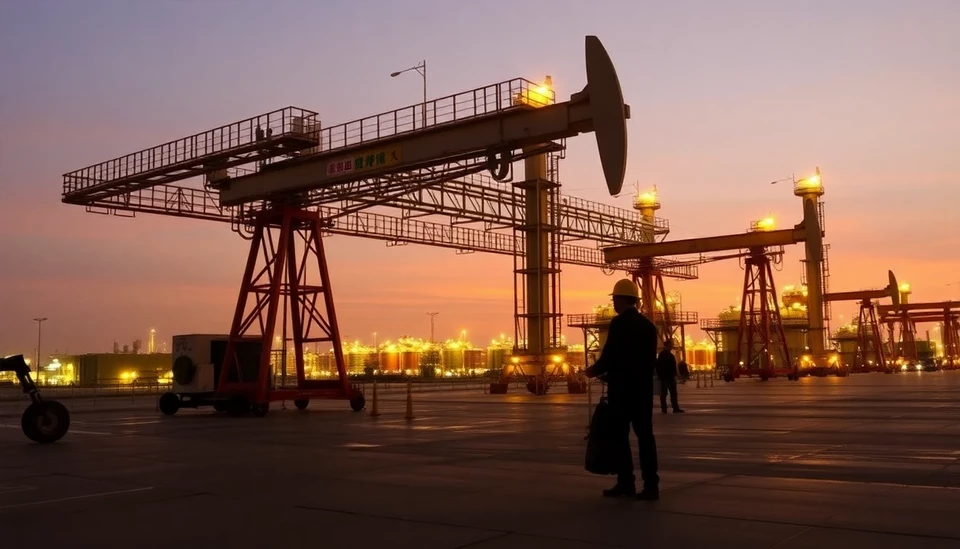
China's oil refining sector is currently facing significant challenges as an overwhelming supply of crude oil is dramatically affecting profitability and prompting several refineries to temporarily reduce operations. The latest reports indicate that refiners are contending with a surplus of domestic fuel, leading to escalated competition and, consequently, economic strain across the industry.
Key players within China’s refining market are struggling to navigate this tumultuous environment characterized by an oversupply of refined products. As the domestic demand for fuel experiences stagnation, excess oil output is resulting in a precarious situation where refiners are unable to maintain their profitability margins. Analysts project that the combination of these factors will force refiners to reconsider their operational strategies in the near future.
Several large state-owned facilities have already indicated plans to cut back on production as a direct response to the declining profit margins. This adjustment comes amid increasing discussions among industry stakeholders regarding the sustainability of current refining practices. With the global market prices exhibiting volatility, refinery operators are finding it increasingly difficult to balance their books without incurring losses.
In a market flooded with surplus, competition has intensified, driving prices down as refiners scramble to sell their products. Fuel stockpiles have surged to levels rarely seen before, putting further pressure on businesses to adjust to a new market reality where oversupply dictates operations. In cities where demand has plateaued or declined, the impact is felt starkly on local economies.
Experts predict that if these conditions persist, we may start to see a wave of consolidations within the sector, where weaker refineries struggle to cope with financial pressures and could potentially be absorbed by their larger counterparts. This reshaping of the industry landscape could result in significant changes in the market dynamics, altering how oil refining operations function across the country.
As the world's largest consumer of crude oil, China’s refining industry plays a crucial role not only in the country's economy but also in global energy markets. A decline in these operations could send ripples throughout the industry, affecting everything from crude oil prices to international trade relations. Stakeholders remain watchful of these developments as they navigate a precariously balanced supply-demand equation in a time of uncertainty.
In conclusion, as Chinese refiners are squeezed by the dual pressures of oversupply and slumping profits, the potential for operational alterations looms large. It will be critical for industry leaders to adopt adaptive strategies that can withstand these evolving challenges to ensure long-term viability and success in a fast-changing market landscape.
#China #OilRefining #Oversupply #ProfitMargins #EnergyMarket #RefineryCuts #MarketDynamics #OilIndustry
Author: John Harris