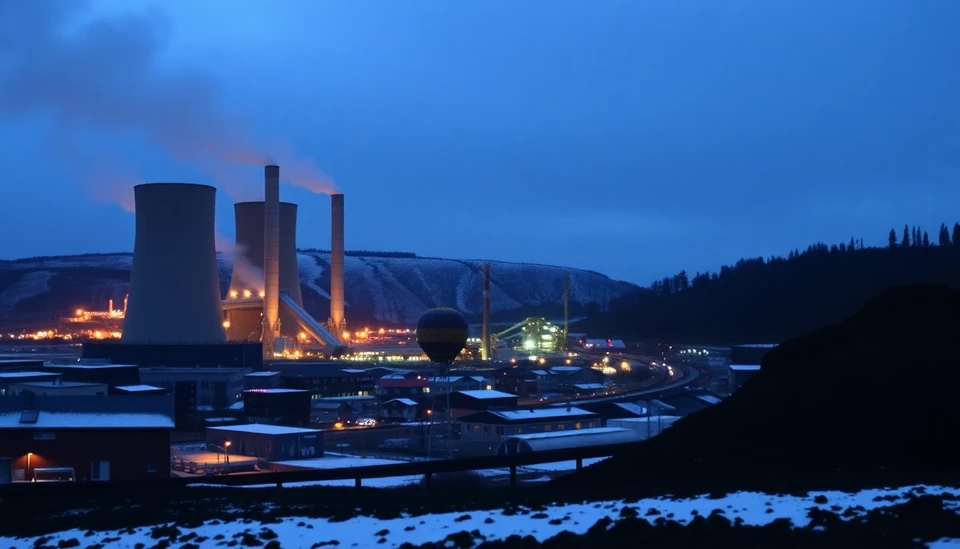
Germany is currently grappling with the pressing issue of its energy transition away from coal, a challenge exacerbated by recent decisions taken by the government in Berlin. The latest report highlights the significant delays that Germany is incurring in its efforts to replace coal with more sustainable energy sources, as the federal government has decided to scrap its plans to expand natural gas infrastructure. This shift in policy is likely to have far-reaching implications for the country’s energy landscape and climate goals.
The rationale behind the decision to abandon the gas plan stems from a growing consensus among environmentalists and policymakers regarding the need to accelerate the shift towards renewable energy. Concerns have been raised that relying on natural gas, which is often viewed as a “bridge fuel,” could undermine the substantial progress made towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions and achieving Germany's climate objectives.
Energy analysts warn that the delay in replacing coal with effective alternatives could lead to increased reliance on fossil fuels in the short term, ultimately threatening Germany’s reputation as a leader in climate action. The cessation of gas projects is seen as a bold move, one that prioritizes the long-term vision of a sustainable energy future over short-term energy security considerations.
Furthermore, the abandonment of the gas plan comes at a precarious time, as Germany is still in the process of reevaluating its overall energy strategy following the geopolitical tensions that have begun to reshape the European energy landscape. The war in Ukraine highlighted the region's vulnerability to energy supply disruptions, leading to a surge in demand for alternative energy supplies. However, Germany's latest shifts indicate a stronger commitment to pivoting toward renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, despite the inherent challenges that accompany this transition.
Germany's postponement of gas infrastructure development has prompted discussions about the potential economic ramifications, particularly in sectors heavily reliant on gas consumption. The move has raised concerns about whether the current frameworks for the implementation of renewable energy can adequately meet the nation’s energy demands without inciting economic hardship or hampering industrial productivity.
The government must now navigate the complexities of this new energy era, including the delicate balance of maintaining energy security while adhering to ambitious climate targets. As Germany's leaders continue to strategize on the best routes to a sustainable energy future, the question remains: will they find a viable path away from coal that does not compromise their economic integrity or energy reliability?
The situation in Germany serves as a critical case study for other nations similarly striving to overcome the transition from fossil fuels. As the world collectively faces the urgent need to address climate change, the decisions made in Germany will likely influence policies and approaches taken by other countries in their energy transitions.
In conclusion, Germany is at a crossroads in its energy policy—a swift transition away from coal and natural gas is essential, but the nation must act decisively and strategically to avoid losing precious time in the fight against climate change.
#Germany #EnergyTransition #ClimateChange #RenewableEnergy #CoalPhaseOut #NaturalGas #Sustainability #EnergyPolicy #GreenEnergy
Author: John Harris