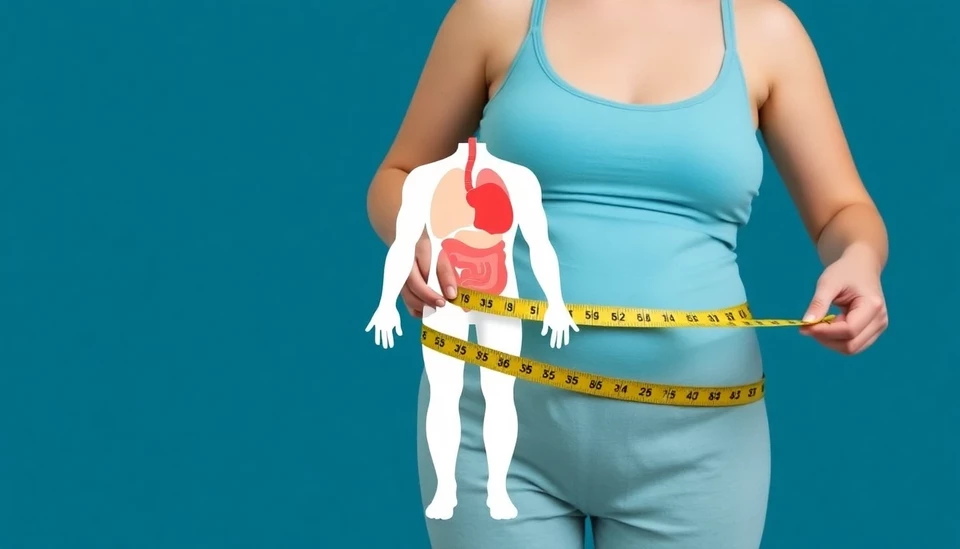
In a groundbreaking development within the medical community, experts are proposing a new benchmark for assessing obesity that significantly departs from the traditional Body Mass Index (BMI). The new approach emphasizes the importance of body fat distribution and overall organ health, giving a comprehensive view of an individual's wellness beyond mere weight metrics. This shift marks a significant advancement in the fight against obesity and its related health complications.
Traditionally, BMI has been the standard tool for measuring obesity, calculated using a person’s weight and height. However, critics argue that BMI fails to account for critical factors such as body composition and fat distribution, which can significantly impact an individual's health. For instance, two individuals with the same BMI may have drastically different levels of body fat and potentially face varying health risks. The adoption of body fat percentage and organ health as benchmarks is poised to address these shortcomings.
Research has increasingly shown that visceral fat, the fat that surrounds the organs, plays a crucial role in determining health outcomes. Its association with various diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome, underscores the need to move beyond BMI as the sole indicator of health. The new guidelines advocate for measuring body fat percentage and evaluating the health of vital organs, such as the heart and liver, to provide a more detailed picture of an individual's health.
Medical experts argue that this holistic approach not only enhances individual health assessments but also aids in tailoring more effective treatment plans. The emphasis on organ health allows for earlier detection of potential health issues and more targeted interventions that can help mitigate the effects of obesity.
Furthermore, the proposed shift reflects a broader movement towards personalized medicine. As understanding of genetics, lifestyle factors, and individual health profiles increases, using tools that consider these variables becomes imperative. This could lead to better prevention strategies and management plans that are customized to each person's unique health profile.
Health professionals see this new focus as a valuable step forward, particularly in educating both patients and practitioners regarding the risks associated with different types of body fat and their locations within the body. The shift towards a more comprehensive understanding of health could also motivate individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles, as they gain a clearer understanding of how their body composition affects their overall well-being.
While adopting the new obesity benchmarks is still in initial discussions, the reception among medical practitioners is largely positive. Many are keen to integrate these arguments into their practices, enhancing their ability to address obesity in a more nuanced and informed manner. With significant implications for both public health and personal health management, this development in obesity assessment heralds a new era in healthcare.
As the medical community awaits further studies and potential formal recommendations, one thing is clear: the emphasis on body fat and organ health could significantly alter the way we perceive and address obesity in the coming years.
#Obesity #BodyFat #Health #BMI #OrganHealth #PublicHealth #PersonalizedMedicine #Wellness
Author: John Harris




